Proximate analysis: Van Soest fiber analysis
|
Principle and Scope
|
|

|
The concept behind the detergent fiber analysis is that plant cells
can be divided into less digestible cell walls (contains hemicellulose,
cellulose and lignin) and mostly digestible cell contents (contains starch and
sugars). Van Soest separated these two components successfully by use of two
detergents: a neutral detergent (Na-lauryl sulfate, EDTA, pH =7.0) and an acid
detergent (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide in 1 N H2SO4).
Hemicellulose,
cellulose and lignin are indigestible in non-ruminants, while Hemicellulose and
Cellulose are partially digestible in ruminants. NDF = Hemicellulose +
Cellulose + Lignin ADF = Cellulose + Lignin
Neutral Detergent Fiber is a
good indicator of "bulk" and thus feed intake. Acid detergent fiber is a good
indicator of digestibility and thus energy intake
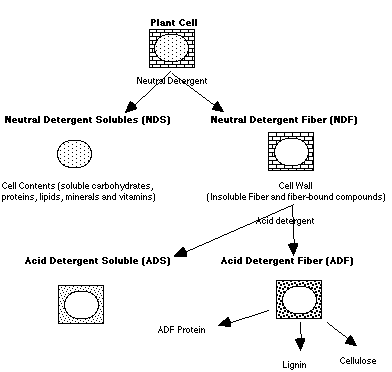 |
| Figure: Principle of detergent partitioning of the fiber fraction
by Van Soest |
Although aquaculture does not deal with ruminants at all, it may be
useful to be aware of these analysis. For instance dealing with plant material
as imortant feed ingredient or dealing with herbivorous fish.
|
Reagents
|
|

|
Reagents for NDF determination (Neutral detergent fiber)
- Neutral detergent solution:
- Sodium borate decahydrate (Na2B4O7 - 10 H2O) 6.81 g
- Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA, C10H14N2Na2O8)
- 18.61 g Sodium lauryl sulfate neutral (C12H25NaO4S)
- 30 g 2-ethoxyethanol (Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, Cellosolve,
C4H10O2)
- 10 ml Disodium phosphate anhydrous (Na2HPO4) 4.56 g
- Distilled water 1000 ml. Pour Sodium borate and disodium EDTA in a
beaker and dissolve with a part of distilled water while heating. Add lauryl
sulfate and 2-ethoxyethanol. Separately dissolve disodium phosphate in part of
distilled water while heating until complete solution is obtained. Mix the two
solutions and the remaining distilled water and control the pH which must be
between 6.9 and 7.1
- 2. n-octanol (C8H18O) octilic alcohol
- 3. Sodium sulfite anhydrous (Na2SO3) 4. Acetone
Reagents for ADF determination (Acid detergent fiber)
- Acid detergent solution:
- Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide technical grade (C19H42BrN) 20 g
- Sulfuric acid 1 N (H2SO4, 49.04 g/l) 1 l
- Dissolve tensioactive into acid while stirring to promote
dissolution.
- n-octanol (C8H18O) octilic alcohol.
- Acetone.
|
Procedure
|
|

|
Procedure for NDF determination (Neutral detergent fiber)
- Grind the air dried sample to pass 1 mm screen.
- Weigh in a crucible 1 g of grinded sample with 1 mg approximation.
- Add 100 ml of neutral detergent solution at room temperature into
crucible with 0.5 g of sodium sulfite and some drops of n-octanol.
- Heat to boiling and reflux 60 minutes from onset of boiling.
- Filter and wash 3 times with boiling water, then twice with cold
acetone.
- Dry 8 hours at 105 °C and let cool in a desiccator.
- Weigh.
- Calculate neutral detergent fiber: NDF % = (weight of crucible +
weight of residue) - weight of crucible / weight of sample x 100. Neutral
detergent solubles: NDS % = 100 - NDF %.
- Ash in a muffle at 550 °C 2 hours and let cool in a desiccator.
- Weigh.
- Calculate ash insoluble in neutral detergent: loss on ashing /
weight of sample x 100.
Procedure for ADF determination (Acid detergent fiber)
- Grind the air dried sample to pass 1 mm screen.
- Weigh in a crucible 1 g of grinded sample with 1 mg approximation.
- Add 100 ml of acid detergent solution at room temperature and some
drops of n-octanol.
- Heat to boiling and reflux 60 minutes from onset of boiling.
- Filter and wash 3 times with boiling water, then twice with cold
acetone.
- Dry 8 hours at 105 °C and let cool in a desiccator.
- Weigh.
- Calculate acid detergent fiber: ADF % = (weight of crucible + weight
of residue) - weight of crucible / weight of sample x 100.
- Ash in a muffle at 550 °C 2 hours and let cool in a desiccator.
- Weigh.
- Calculate ash insoluble in acid detergent: loss on ashing / weight
of sample x 100.
|
